검색결과 리스트
전체보기에 해당되는 글 1767건
- 2023.02.11 백준 18108번 1998년생인 내가 태국에서는 2541년생?!(C#, JAVA)
- 2023.02.11 백준 C#, JAVA 10926번 아이디 string 뒤에 ??! 붙이기
- 2023.02.11 프로그래머스 레벨2 C# 연속 부분 수열 합의 개수(Hash.Count, HashSet, Skip, Take, JAVA)
- 2023.02.11 프로그래머스 C# 행렬의 곱셈(3중 for문, JAVA)
- 2023.02.11 프로그래머스 C# 예상 대진표(JAVA)
- 2023.02.11 프로그래머스 문자열 내의 p와 y의 개수(JAVA, toLowerCase().split(""), equals)
- 2023.02.11 백준 JAVA, C# 10089번 사칙연산, 나머지 구하기
- 2023.02.11 백준 JAVA, C# 1008번 나눗셈
글
백준 18108번 1998년생인 내가 태국에서는 2541년생?!(C#, JAVA)

using System;
namespace Baekjoon {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int a = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(a-543);
}
}
}
//////////////
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a - 543);
}
}
'백준 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 10430번 나머지(JAVA, C#) (0) | 2023.02.12 |
|---|---|
| 백준 3003번 JAVA, C# (킹, 퀸, 룩, 비숍, 나이트, 폰) (0) | 2023.02.12 |
| 백준 C#, JAVA 10926번 아이디 string 뒤에 ??! 붙이기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 10089번 사칙연산, 나머지 구하기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 1008번 나눗셈 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
글
백준 C#, JAVA 10926번 아이디 string 뒤에 ??! 붙이기
using System;
namespace Baekjoon {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
string s = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine(s + "??!");
}
}
}
//////
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = sc.next();
System.out.println(a + "??!");
}
}
'백준 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 3003번 JAVA, C# (킹, 퀸, 룩, 비숍, 나이트, 폰) (0) | 2023.02.12 |
|---|---|
| 백준 18108번 1998년생인 내가 태국에서는 2541년생?!(C#, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 10089번 사칙연산, 나머지 구하기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 1008번 나눗셈 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 2557번 (0) | 2023.02.10 |
글
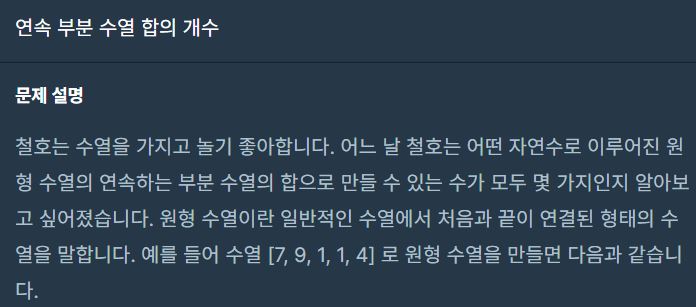
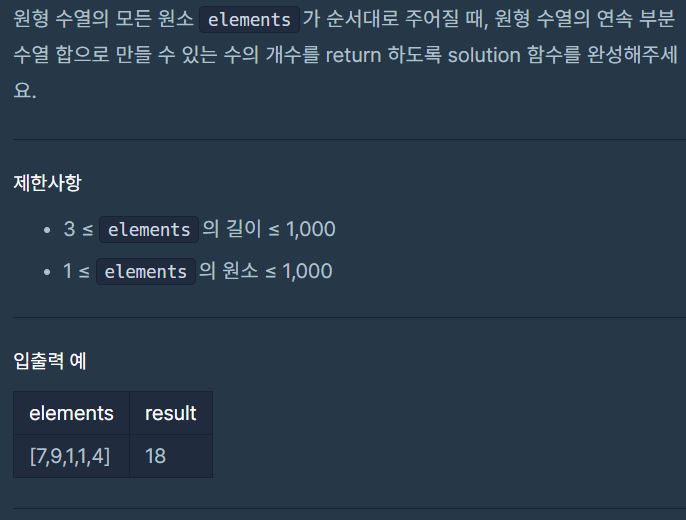
프로그래머스 레벨2 C# 연속 부분 수열 합의 개수(Hash.Count, HashSet, Skip, Take, JAVA)


/// 내가 작성한 코드
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Solution {
public int solution(int[] elements) {
int[] doublearray = new int[2 * elements.Length];
/// 2배 길이의 배열을 작성해서 뒤에서 앞으로 합계를 구하는 경우가 가능하게 했다.
HashSet<int> hash = new HashSet<int>(); // 중복 저장이 불가능한 HashSet을 썼다.
for(int i = 0;i<2*elements.Length;i++)
{
doublearray[i] = elements[i%elements.Length];
}
/// 2배 배열을 대입
for(int i = 0;i<elements.Length;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j<elements.Length;j++)
{
int[] newArray = doublearray.Skip(i).Take(j+1).ToArray();
hash.Add(newArray.Sum());
}
}
return hash.Count;
}
}
// 되기는 되는데 시간이 엄청나게 오래 걸려서 겨우겨우 실행이 됐다. 그래서 다른 분 코드를 참조한 것을 했다.
// skip부터 시작해서 take에 있는 숫자 만큼 취한다.
//
//
//
//
using System;
public class Solution {
public int solution(int[] elements)
{
int answer = 0;
int[] flagedInts = new int[elements.Length * 1000 + 1]; // 100만개까지 배열을 만든다. 길이가 1000이고, 배열에 들어가는 수가 1000까지니까 최대가 1000 * 1000 = 100만개까지 나온다. 전부 0이 들어가 있다.
for(int addingLen = 1; addingLen <= elements.Length; addingLen++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < elements.Length; i++)
{
int idx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < addingLen; j++)
{
idx += elements[(i + j) % (elements.Length)];
}
// 선택된 배열 인덱스만 1을 집어넣게 해서 if문으로 중복을 걸러내고 answer의 값을 플러스 시켜서 갯수를 구한다.
if (flagedInts[idx] == 0)
{
flagedInts[idx] = 1;
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}
// 이게 시간이 훨씬 덜 나온다.
자바
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] elements) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
int start = 1;
while(start < elements.length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < elements.length; i++)
{
int value = 0;
for (int j = i; j < i+start; j++)
{
value += elements[j%elements.length];
}
set.add(value);
}
start++;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < elements.length; i++)
sum += elements[i];
set.add(sum);
return set.size();
}
}
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] elements) {
int answer = 0;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
int start = 0;
for(int i=0; i<elements.length; i++)
{
int n = 1;
int idx = i;
int sum = 0;
while(n <= elements.length)
{
sum += elements[idx++];
set.add(sum);
if(idx >= elements.length)
idx = 0;
n++;
}
}
answer = set.size();
return answer;
}
}'프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 주식가격 C#(JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.23 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 뒤에 있는 큰 수 찾기 C#(JAVA) peek, pop, push (0) | 2023.02.23 |
| 프로그래머스 C# 행렬의 곱셈(3중 for문, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 C# 예상 대진표(JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 문자열 내의 p와 y의 개수(JAVA, toLowerCase().split(""), equals) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
글
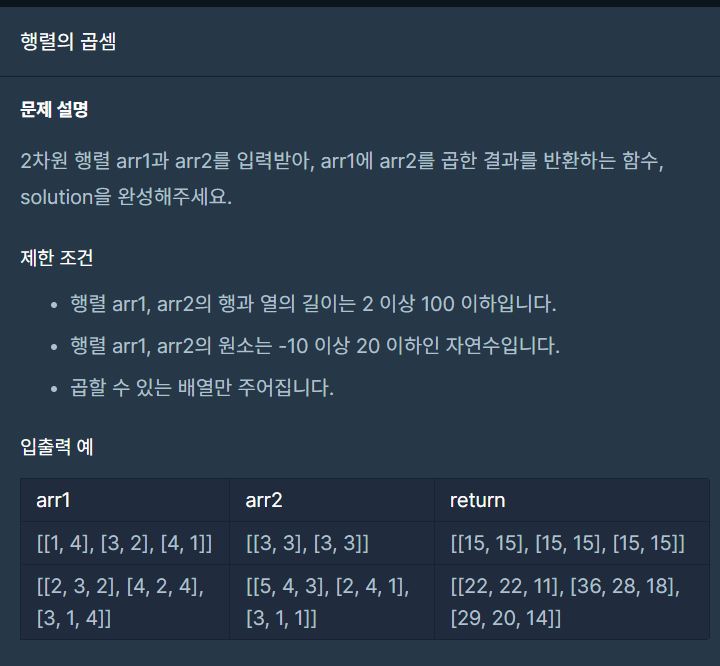
프로그래머스 C# 행렬의 곱셈(3중 for문, JAVA)
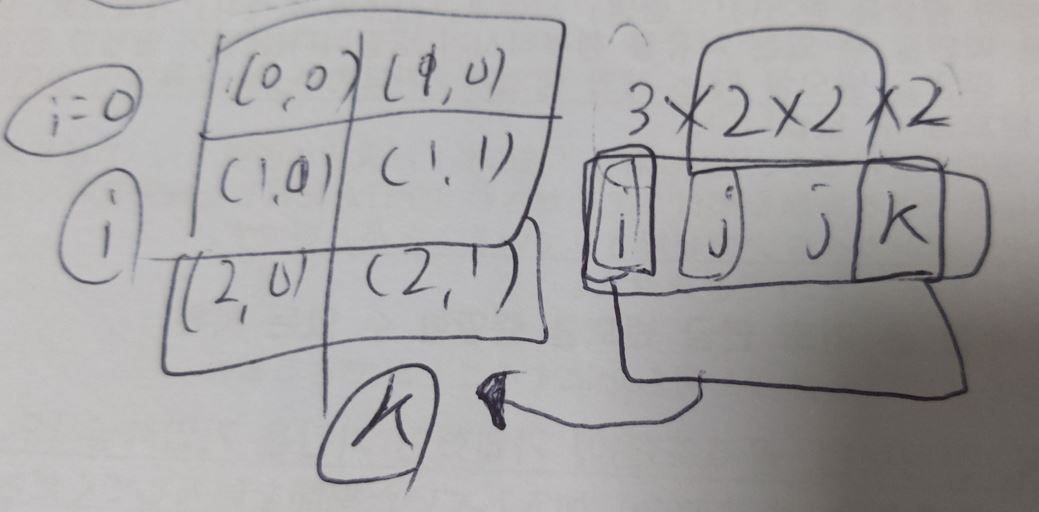
using System;
public class Solution {
public int[,] solution(int[,] arr1, int[,] arr2) {
int[,] answer = new int[arr1.GetLength(0),arr2.GetLength(1)];
for(int i = 0;i<arr1.GetLength(0);i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j<arr2.GetLength(0);j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < arr2.GetLength(1); k++)
{
answer[i, k] += arr1[i, j] * arr2[j, k];
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}
자바
class ProductMatrix {
public int[][] productMatrix(int[][] A, int[][] B) {
int[][] answer = new int[A.length][B[0].length];
for(int i=0;i<answer.length;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<answer[0].length;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<A[0].length;k++)
{
answer[i][j]+=A[i][k]*B[k][j];
}
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductMatrix c = new ProductMatrix();
int[][] a = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 } };
int[][] b = { { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 } };
// 아래는 테스트로 출력해 보기 위한 코드입니다.
System.out.println("행렬의 곱셈 : " + c.productMatrix(a, b));
}
}
'프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 뒤에 있는 큰 수 찾기 C#(JAVA) peek, pop, push (0) | 2023.02.23 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 C# 연속 부분 수열 합의 개수(Hash.Count, HashSet, Skip, Take, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 C# 예상 대진표(JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 문자열 내의 p와 y의 개수(JAVA, toLowerCase().split(""), equals) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 JAVA 폰켓몬 (0) | 2023.02.09 |
글
프로그래머스 C# 예상 대진표(JAVA)

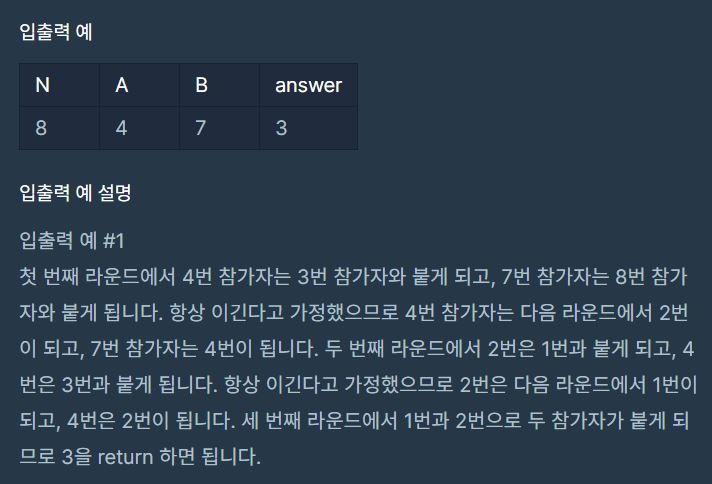
using System;
class Solution
{
public int solution(int n, int a, int b)
{
int answer = 0;
int index = 0;
/// a를 2로 나눈 몫+나머지, b를 2로 나눈 몫+나머지
while(a != b)
{
index++;
a = a/2+a%2;
b = b/2+b%2;
}
return index;
}
}
/// 라운드에서 위로 올라갈 때마다 번호가 바뀌는 방법을 응용했다.
자바
class Solution
{
public int solution(int n, int a, int b)
{
int round = 0;
while(a != b)
{
a = a/2 + a%2;
b = b/2 + b%2;
round++;
}
return round;
}
}
class Solution
{
public int solution(int n, int a, int b)
{
return Integer.toBinaryString((a-1)^(b-1)).length();
}
}'프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 C# 연속 부분 수열 합의 개수(Hash.Count, HashSet, Skip, Take, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 C# 행렬의 곱셈(3중 for문, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 문자열 내의 p와 y의 개수(JAVA, toLowerCase().split(""), equals) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 JAVA 폰켓몬 (0) | 2023.02.09 |
| 프로그래머스 레벨0 안전지대(C#, JAVA) try catch(Exception e) (0) | 2023.02.09 |
글
프로그래머스 문자열 내의 p와 y의 개수(JAVA, toLowerCase().split(""), equals)
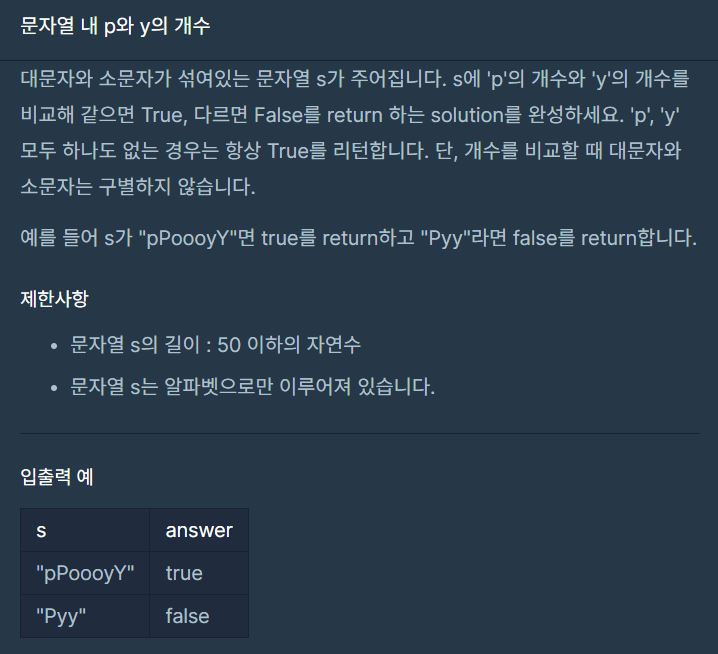
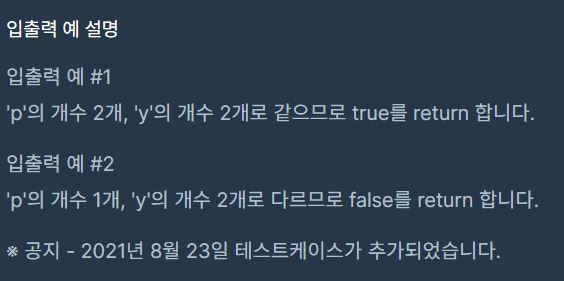
class Solution {
boolean solution(String s) {
int pCount = 0, yCount = 0;
String[] array = s.toLowerCase().split(""); //소문자로 바꾸고 잘라 배열에 넣음
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
if ("p".equals(array[i]))
{
pCount++;
}
else if ("y".equals(array[i]))
{
yCount++;
}
}
if (pCount != yCount)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
'프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 C# 행렬의 곱셈(3중 for문, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 C# 예상 대진표(JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 프로그래머스 JAVA 폰켓몬 (0) | 2023.02.09 |
| 프로그래머스 레벨0 안전지대(C#, JAVA) try catch(Exception e) (0) | 2023.02.09 |
| 다항식 더하기 JAVA (0) | 2023.02.09 |
글
백준 JAVA, C# 10089번 사칙연산, 나머지 구하기
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a, b;
a = sc.nextInt();
b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a + b);
System.out.println(a - b);
System.out.println(a * b);
System.out.println(a / b);
System.out.println(a % b);
}
}
/////////////
using System;
namespace Baekjoon {
class Program {
static void Main() {
string s = Console.ReadLine();
string[] ss = s.Split();
int a = int.Parse(ss[0]);
int b = int.Parse(ss[1]);
Console.WriteLine(a+b);
Console.WriteLine(a-b);
Console.WriteLine(a*b);
Console.WriteLine(a/b);
Console.WriteLine(a%b);
}
}
}
'백준 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 18108번 1998년생인 내가 태국에서는 2541년생?!(C#, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
|---|---|
| 백준 C#, JAVA 10926번 아이디 string 뒤에 ??! 붙이기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 1008번 나눗셈 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 2557번 (0) | 2023.02.10 |
| 백준 A+B, A-B, A*B JAVA, C# (0) | 2023.02.10 |
글
백준 JAVA, C# 1008번 나눗셈
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Double a, b;
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println(a + b);
}
}
///////////////
using System;
namespace Baekjoon {
class Program {
static void Main() {
string s = Console.ReadLine();
string[] ss = s.Split();
Double a = int.Parse(ss[0]);
Double b = int.Parse(ss[1]);
Console.WriteLine(a/b);
}
}
}
'백준 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 18108번 1998년생인 내가 태국에서는 2541년생?!(C#, JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.11 |
|---|---|
| 백준 C#, JAVA 10926번 아이디 string 뒤에 ??! 붙이기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 10089번 사칙연산, 나머지 구하기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
| 백준 JAVA, C# 2557번 (0) | 2023.02.10 |
| 백준 A+B, A-B, A*B JAVA, C# (0) | 2023.02.10 |